World War I, often referred to as the Great War, spanned from 1914 to 1918 and reshaped the course of the 20th century. Its impact reverberated across continents, bringing about lasting political and cultural change. But, beyond the well-known stories and statistics, there are myriad lesser-known facts that provide fascinating insights into the world of a century ago. Here are 40 intriguing details you may not know about WWI.
 Image by Mohamed Hassan from Pixabay
Image by Mohamed Hassan from Pixabay
1. Unexpected Assassin
Gavrilo Princip, the man who assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand (thus sparking the war), was only able to do so because he happened to be eating a sandwich near where the Archduke's car took a wrong turn.
 Image by Heriberto Aguirre from Pixabay
Image by Heriberto Aguirre from Pixabay
2. First Use of Tanks
Tanks were first used in battle during WWI by the British at the Battle of Flers-Courcelette in 1916.
3. Wartime Plastic Surgery
WWI saw the first significant use of plastic surgery due to the devastating facial injuries from trench warfare.
 Image by 10634669 from Pixabay
Image by 10634669 from Pixabay
4. Pigeon Heroes
Pigeons played crucial roles in delivering messages. One famous pigeon, Cher Ami, saved nearly 200 men by delivering a critical message despite being injured.
 Image by Thiago de Paula Oliveira from Pixabay
Image by Thiago de Paula Oliveira from Pixabay
5. Glowing Wounds
Some soldiers reported their wounds glowing in the dark, a phenomenon later attributed to the bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens, which likely reduced wound infections.
 Image by Mohamed Hassan from Pixabay
Image by Mohamed Hassan from Pixabay
6. Author in the Trenches
J.R.R. Tolkien, the author of "The Lord of the Rings," served during WWI and said it influenced his writings.
 Image by Annie Spratt from Pixabay
Image by Annie Spratt from Pixabay
7. Unbreakable Code
The Choctaw Telephone Squad used their native language as a code, which the Germans never broke.
 Image by Boskampi from Pixabay
Image by Boskampi from Pixabay
8. Deadly Spanish Flu
More U.S. soldiers died from the 1918 Spanish flu than were killed in battle during the war.
 Image by Dennis Larsen from Pixabay
Image by Dennis Larsen from Pixabay
9. Artificial Fog
To hide their movements, soldiers sometimes released large amounts of smoke to create artificial fog.
 Image by Dariusz Sankowski from Pixabay
Image by Dariusz Sankowski from Pixabay
10. War's Deadliest Day
The first day of the Battle of the Somme remains Britain's single deadliest day, with nearly 20,000 soldiers killed.
11. Silent Night
On Christmas Day 1914, some German and British troops held an unofficial ceasefire, playing football and exchanging gifts.
 Image by KEREM TAŞER from Pixabay
Image by KEREM TAŞER from Pixabay
12. First Female Soldiers
Russia was the only nation to use female combat troops in frontline roles during WWI.
 Image by Dimitris Vetsikas from Pixabay
Image by Dimitris Vetsikas from Pixabay
13. The Lost Generation
The term "Lost Generation," popularized by Hemingway, originated from Gertrude Stein and referred to those who grew up during the war and suffered its traumas.
 Image by Dimitris Vetsikas from Pixabay
Image by Dimitris Vetsikas from Pixabay
14. Brief Naval Battles
Despite the massive naval arms race before 1914, there were very few direct naval confrontations between the major powers during the war.
15. Rise of Plastic
The war accelerated the use of plastic materials as they became essential for various applications, from aircraft to medical equipment.
 Image by fernando zhiminaicela from Pixabay
Image by fernando zhiminaicela from Pixabay
16. Conscription Ages
In Britain, men between 18 and 41 were subject to conscription, with some exceptions.
17. Not World-wide
Despite being called a "World War," over 20 countries remained neutral throughout the conflict.
18. Dazzling Camouflage
Some ships were painted with bold geometric patterns, called "Dazzle Camouflage," to confuse enemy ships.
 Image by DarlinDona from Pixabay
Image by DarlinDona from Pixabay
19. First Air Raid
The first air raid on Britain was carried out by German Zeppelin airships, not airplanes.
 Image by Vicki Hamilton from Pixabay
Image by Vicki Hamilton from Pixabay
20. The Harlem Hellfighters
An African-American regiment, the 369th Infantry Regiment, fought valiantly for France and became one of the war's most decorated units.
 Image by Henryk Niestrój from Pixabay
Image by Henryk Niestrój from Pixabay
21. License to Kill
Soldiers could request a "white feather" to be sent to a man not in uniform as a symbol of cowardice. This led to public humiliation and, in many cases, enlistment.
 Image by alba1970 from Pixabay
Image by alba1970 from Pixabay
22. War and Fashion
Trench coats and wristwatches, now fashion staples, gained popularity because of their practicality during the war.
 Image by SplitShire from Pixabay
Image by SplitShire from Pixabay
23. Journalist Imprisonment
Edith Cavell, a British nurse and journalist, was executed by the Germans for helping soldiers escape occupied Belgium.
 Image by Tayeb MEZAHDIA from Pixabay
Image by Tayeb MEZAHDIA from Pixabay
24. Largest Cannon Ever
The German Big Bertha was one of the largest cannons ever used in warfare, able to launch 820 kg projectiles.
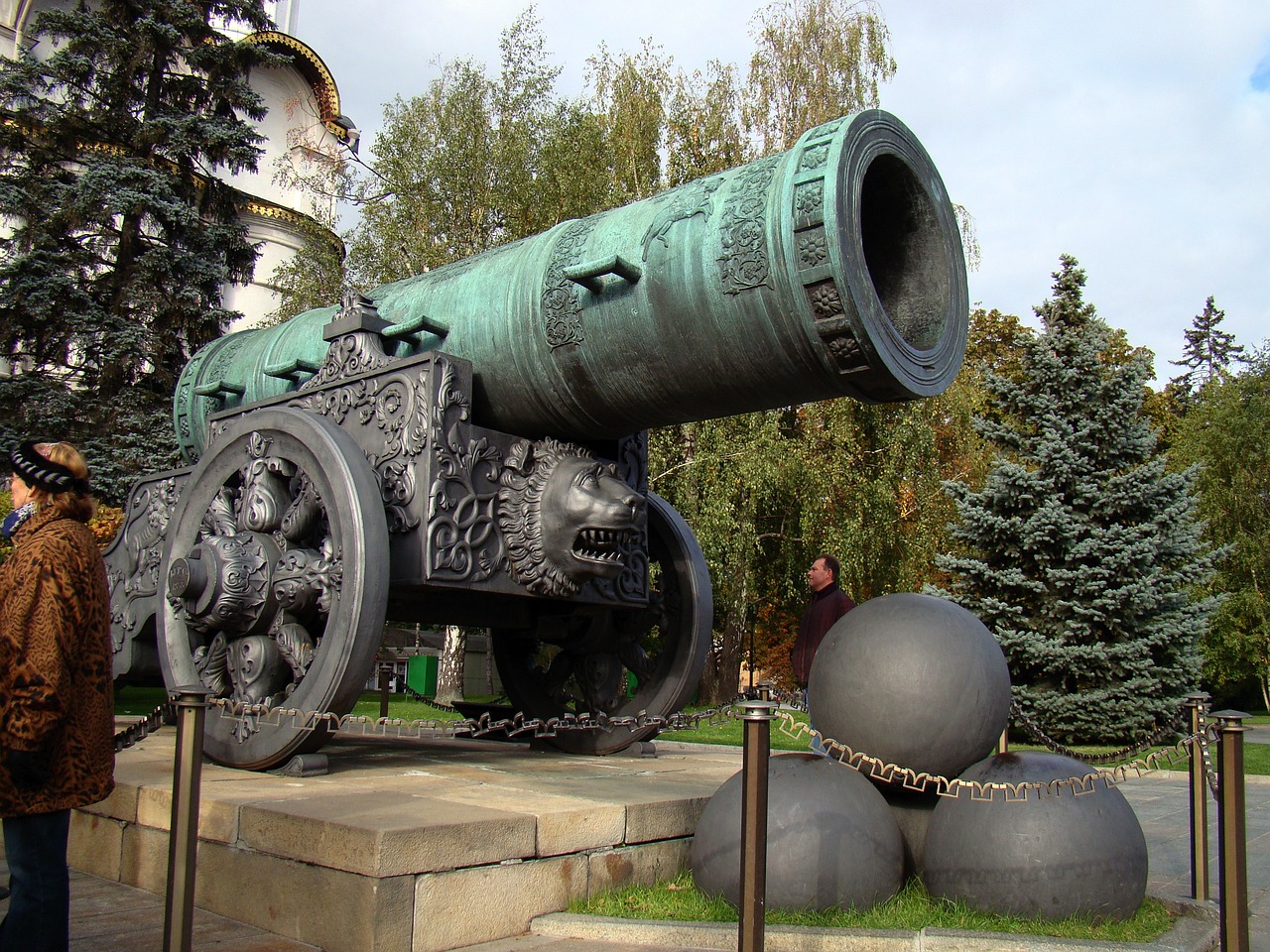 Image by Tatyana Kazakova from Pixabay
Image by Tatyana Kazakova from Pixabay
25. The Red Baron
The most famous fighter pilot of the war, Manfred von Richthofen, was credited with 80 air combat victories.
 Image by eagletonc from Pixabay
Image by eagletonc from Pixabay
26. Youngest Soldier
The youngest known soldier to serve was only 12 years old – a boy named Sidney Lewis from Britain.
 Image by Thomas Rüdesheim from Pixabay
Image by Thomas Rüdesheim from Pixabay
27. Soccer in No Man's Land
Soldiers from both sides occasionally played soccer in no man's land during pauses in battle.
 Image by Welcome to All ! ツ from Pixabay
Image by Welcome to All ! ツ from Pixabay
28. Literary Officers
Many of the 20th century's greatest writers served in WWI, including Ernest Hemingway, Siegfried Sassoon, and Robert Graves.
 Image by Anne and Saturnino Miranda from Pixabay
Image by Anne and Saturnino Miranda from Pixabay
29. The Original "War to End All Wars"
WWI was optimistically referred to as the "war to end all wars," a sentiment echoed by President Woodrow Wilson.
 Image by Robert Waghorn from Pixabay
Image by Robert Waghorn from Pixabay
30. Airplanes' Limited Role
At the war's outset, airplanes were used mainly for reconnaissance. Their role as fighters and bombers developed as the war progressed.
 Image by Defence-Imagery from Pixabay
Image by Defence-Imagery from Pixabay
31. War by Many Names
Before being called World War I, it was referred to as the Great War, the World War, and even the War of the Nations.
 Image by Michal Jarmoluk from Pixabay
Image by Michal Jarmoluk from Pixabay
32. Tanks' Initial Name
Tanks were initially called "landships." The term "tank" was used as a code name to maintain secrecy.
 Image by Michael Drummond from Pixabay
Image by Michael Drummond from Pixabay
33. The War's Only Undisputed Ace
Belgian pilot Willy Coppens was the only pilot to become an ace solely by shooting down enemy balloons.
 Image by Rudy and Peter Skitterians from Pixabay
Image by Rudy and Peter Skitterians from Pixabay
34. A War of Innovation
Many technologies were developed or popularized during WWI, including sonar, drones, and mobile X-ray machines.
 Image by Thomas Ehrhardt from Pixabay
Image by Thomas Ehrhardt from Pixabay
35. Non-human Casualties
Over 8 million horses died during WWI, highlighting the extensive use and reliance on cavalry and transport.
36. Expanding Female Workforce
The war led to a significant increase in the number of women in the workforce, taking roles traditionally held by men.
 Image by Dimitris Vetsikas from Pixabay
Image by Dimitris Vetsikas from Pixabay
37. Unexpected Peace Treaty Venue
The Treaty of Versailles, which officially ended the war, was signed in the Hall of Mirrors in the Palace of Versailles.
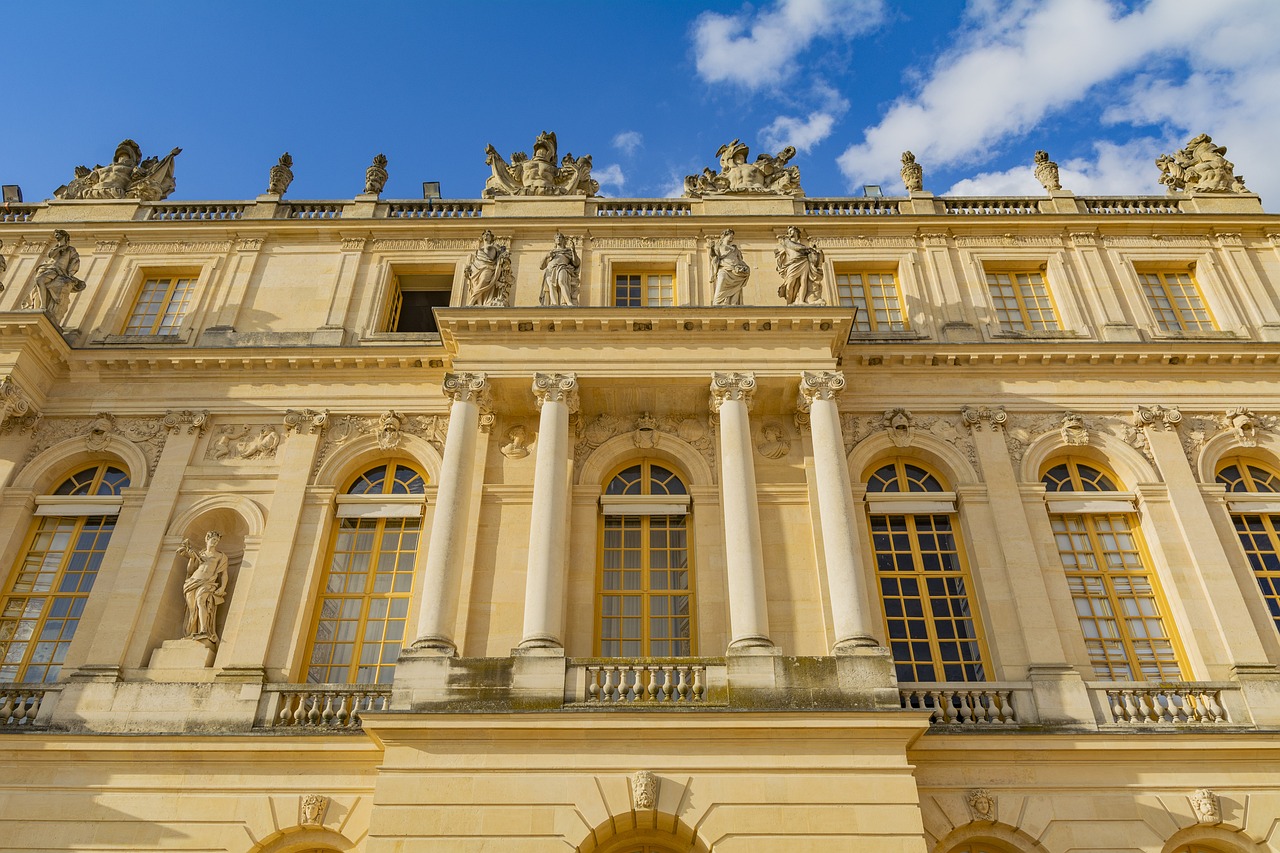 Image by Valdas Miskinis from Pixabay
Image by Valdas Miskinis from Pixabay
38. A World War Baby Boom
After the war ended in 1918, there was a notable baby boom in several countries as soldiers returned home.
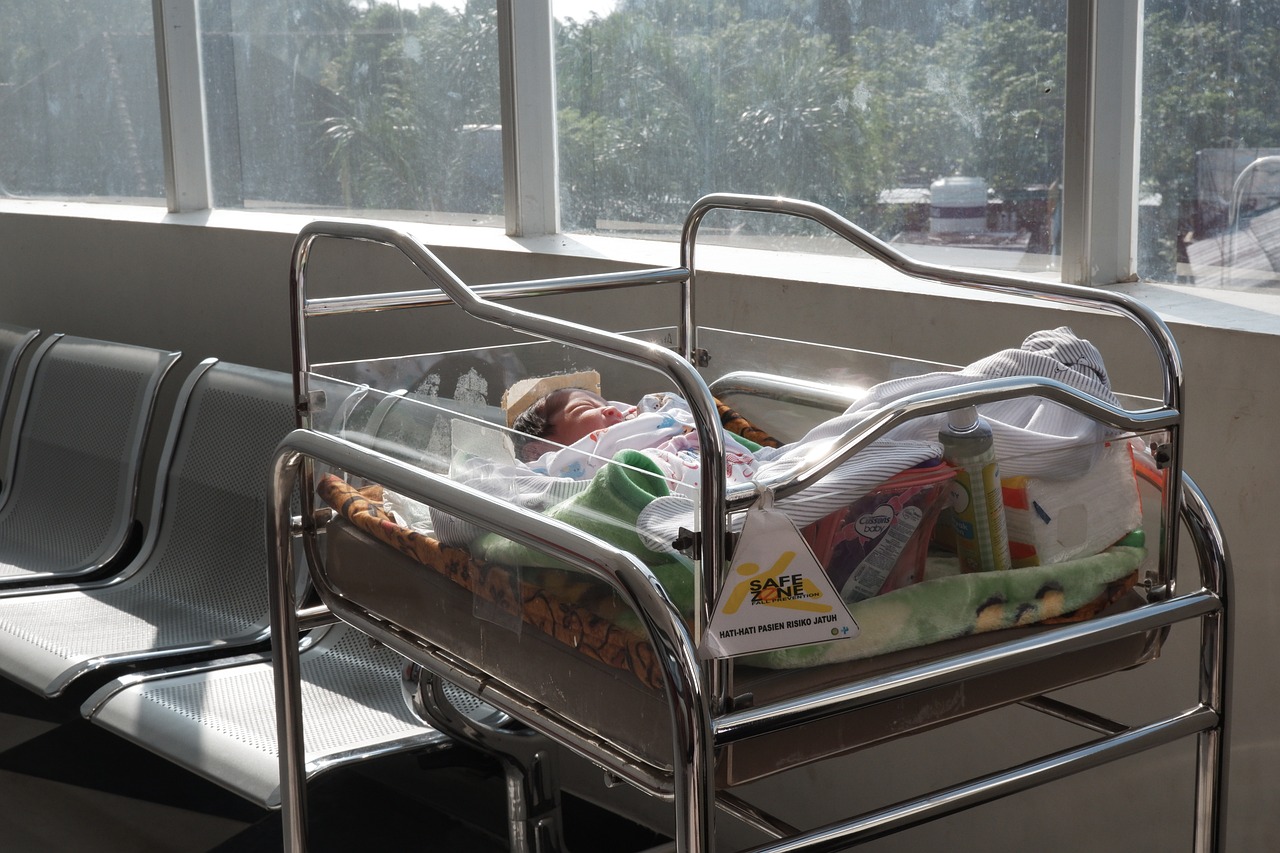 Image by paspornomer1 from Pixabay
Image by paspornomer1 from Pixabay
39. Last Surviving Veteran
The last known combat veteran of WWI, Claude Choules, passed away in 2011 at the age of 110.
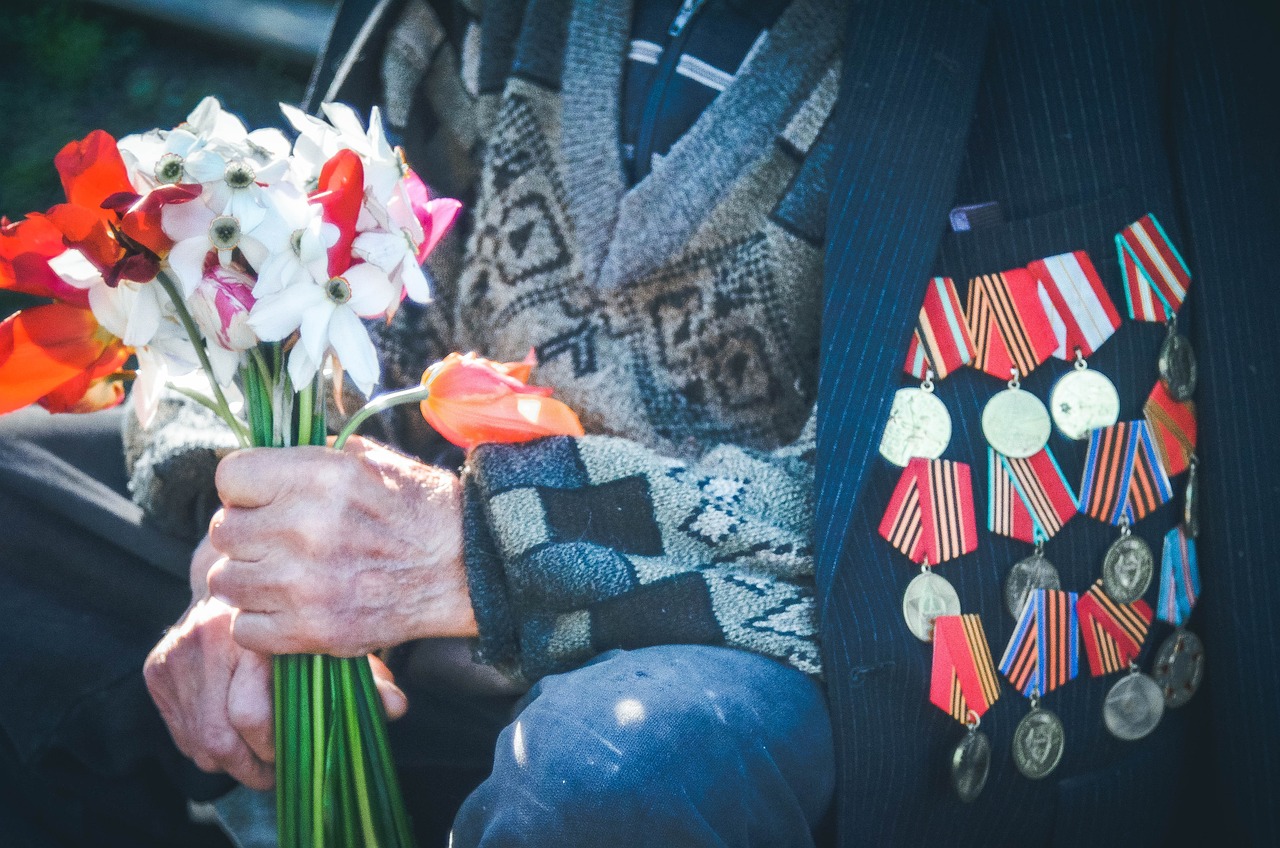 Image by Мария Ткачук from Pixabay
Image by Мария Ткачук from Pixabay
40. A Delayed American Entry
The U.S. did not enter the war until 1917, three years after it began, despite the sinking of the Lusitania in 1915.
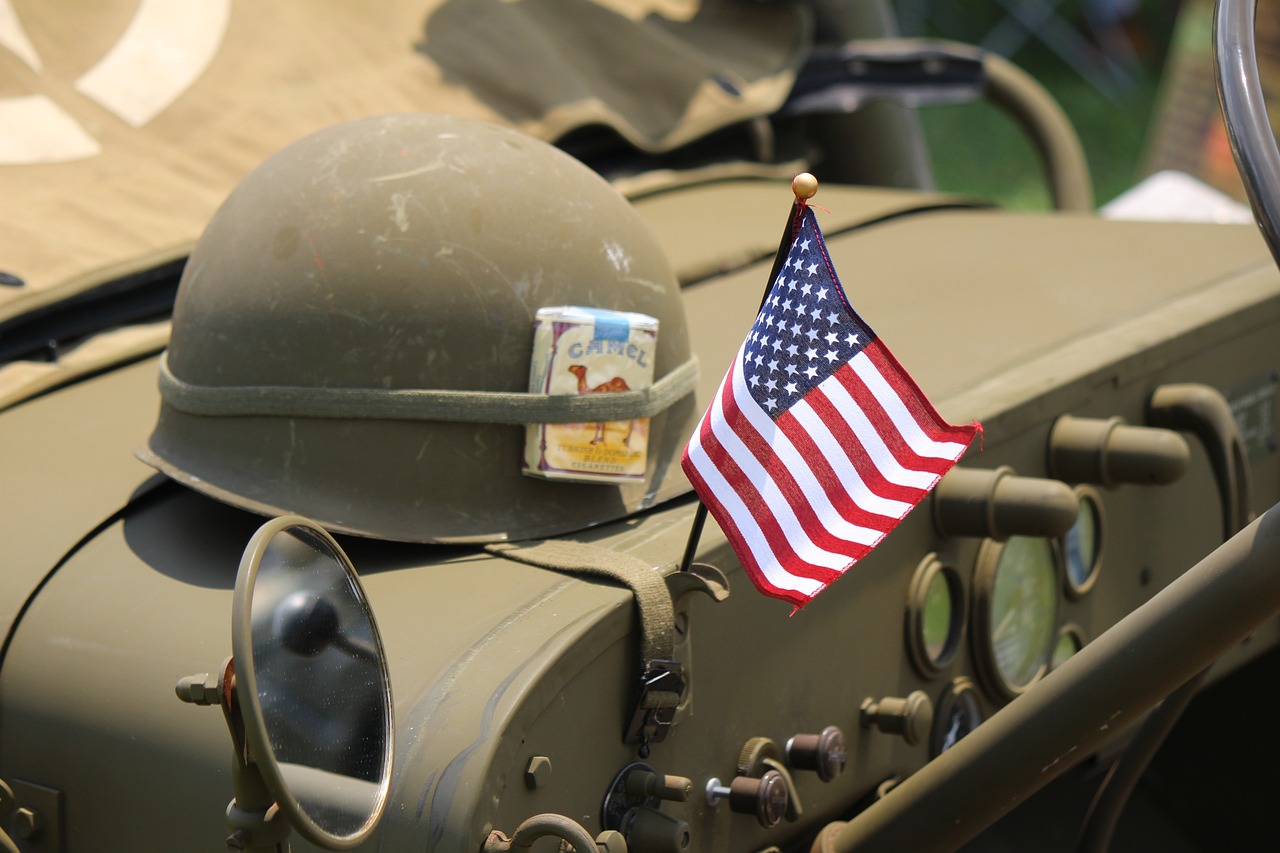 Image by Zack Culver from Pixabay
Image by Zack Culver from Pixabay
From the tragic to the surprising, the Great War was a complex web of events, innovations, and individual stories. These lesser-known facts offer a fresh perspective on one of history's most profound conflicts.