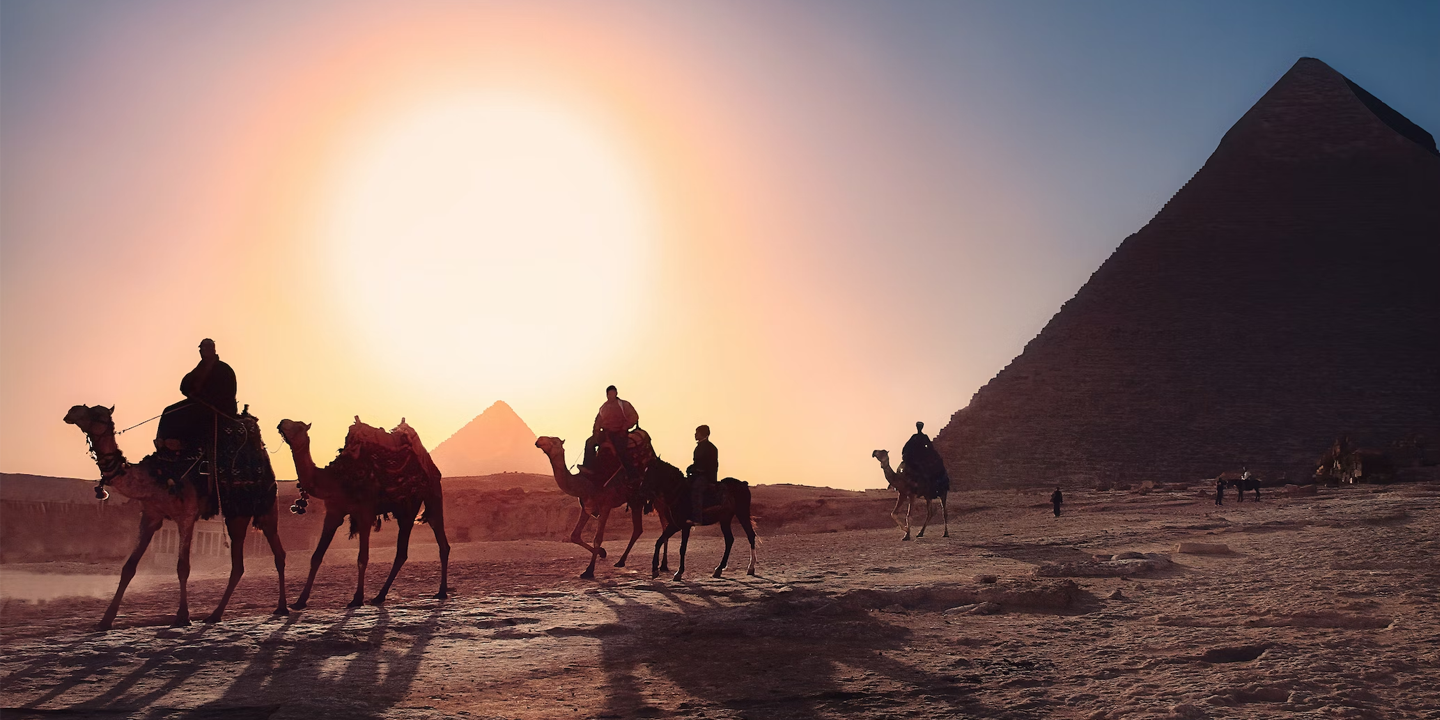
Today, let's take a moment to revisit history and explore the stunning and interesting period of Ancient Egypt. From pyramids to pharaohs to myths and legends, there are so many amazing facts worth learning about. Trust us, you won't leave this article disappointed!
 Photo by Wolfgang Hasselmann on Unsplash
Photo by Wolfgang Hasselmann on Unsplash
1. The Mummy's Curse
Ancient Egyptians believed in the "Curse of the Pharaohs," which was a punishment for anyone who disturbed a mummy's tomb. This legend continues to exist today, with tales of bad luck befalling those who remove artifacts.
 https://unsplash.com/photos/_r9XDE_KFuM
https://unsplash.com/photos/_r9XDE_KFuM
2. Inventors of Makeup
Both men and women in ancient Egypt wore makeup, such as eyeliner and lipstick. It was believed to have protective properties and was also a sign of status.
 Photo by Chalo Garcia on Unsplash
Photo by Chalo Garcia on Unsplash
3. The Great Pyramid Precision
The Great Pyramid of Giza aligns almost perfectly with the cardinal points of the compass. Its precise alignment has created much curiousity as it remains a mystery to this day.
 Photo by Fynn schmidt on Unsplash
Photo by Fynn schmidt on Unsplash
4. Calendar Innovators
The Egyptians created a 365-day calendar based on their observations of the star, Sirius. It's amazing how this system is very close to our current calendar system.
 Photo by FREDDY CANAVIRI APAZA on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by FREDDY CANAVIRI APAZA on Wikimedia Commons
5. Dentistry Pioneers
Ancient Egyptians suffered from dental issues due to their sandy diet. They had a form of dentistry and even had dental bridges.
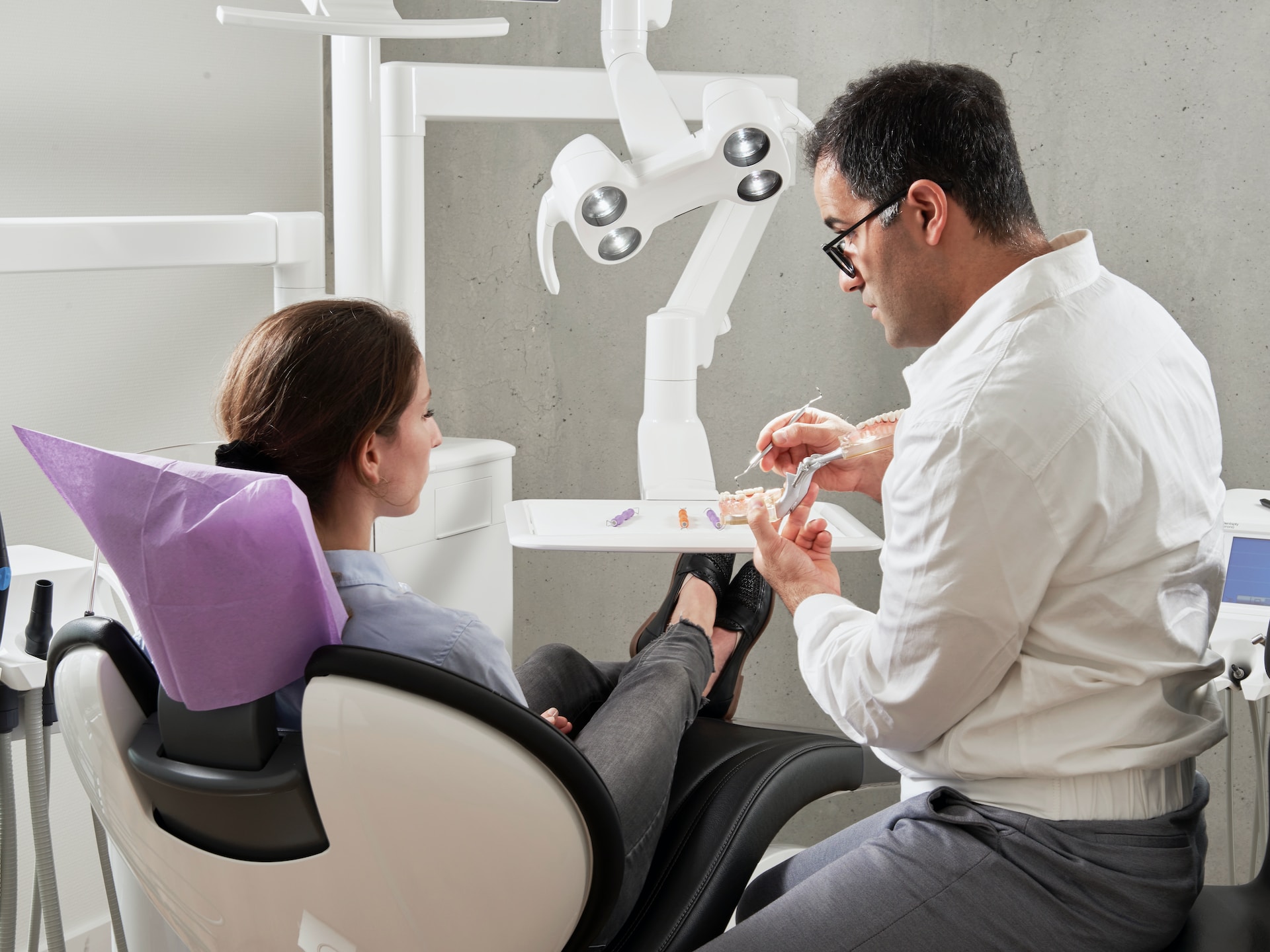 Photo by Caroline LM on Unsplash
Photo by Caroline LM on Unsplash
6. Beekeeping and Honey
Honey was highly prized in ancient Egypt for its sweet taste and medicinal properties. Egyptians practiced beekeeping and used beeswax in various applications.
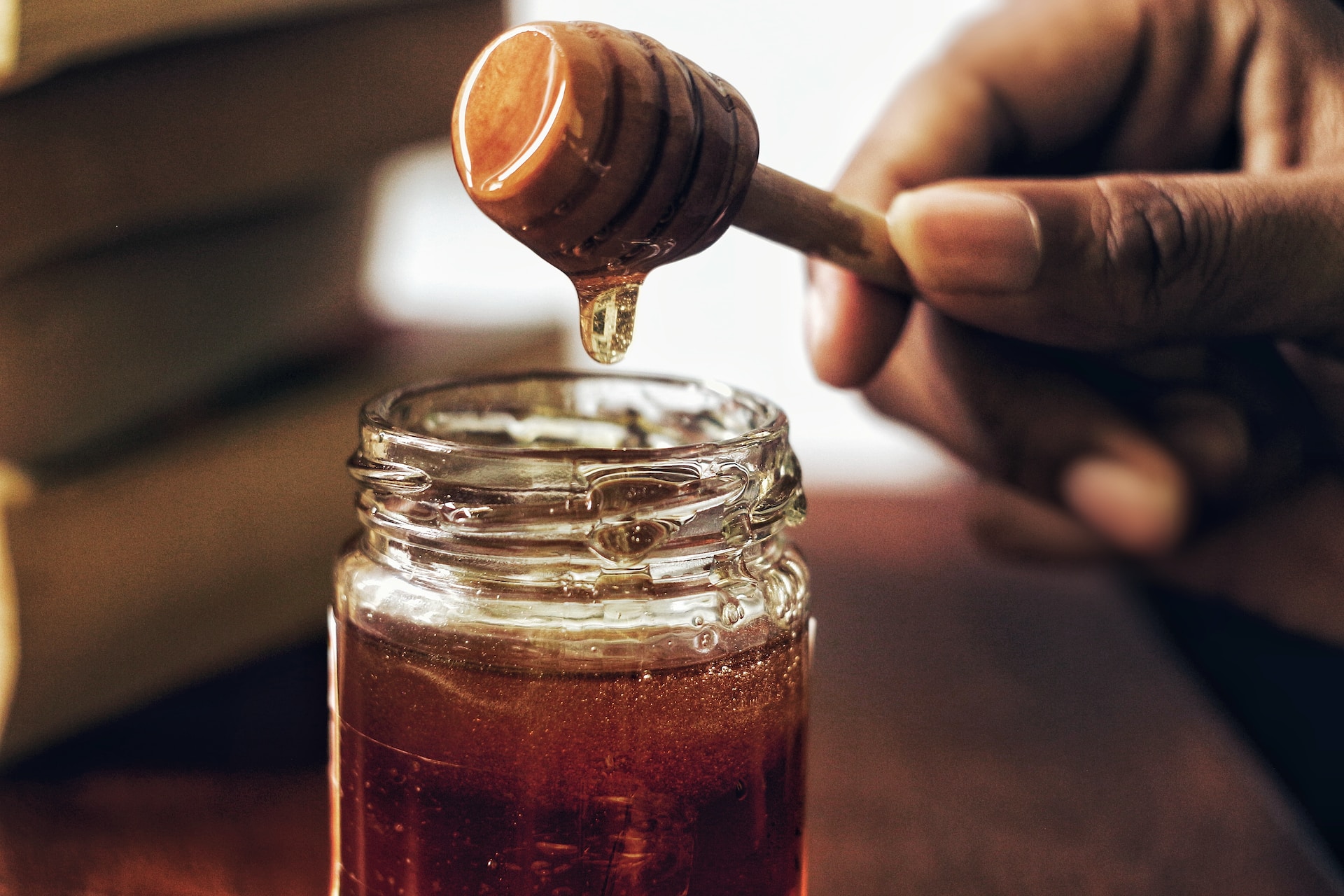 Photo by Arwin Neil Baichoo on Unsplash
Photo by Arwin Neil Baichoo on Unsplash
7. World’s First Peace Treaty
The Egyptians signed one of the world's first recorded peace treaties with the Hittites around 1259 B.C. Both empires sought to establish peace after years of conflict.
 Photo by Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg) on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg) on Wikimedia Commons
8. Nile's Gifts
The Nile River flooded annually, depositing nutrient-rich silt that made the surrounding lands incredibly fertile. This allowed Egypt to become an agricultural powerhouse.
 Photo by Yusef El Gzzar on Unsplash
Photo by Yusef El Gzzar on Unsplash
9. Board Games Aficionados
Ancient Egyptians loved board games, with "Senet" being one of the most popular. It was played by all classes and is often depicted in tomb paintings.
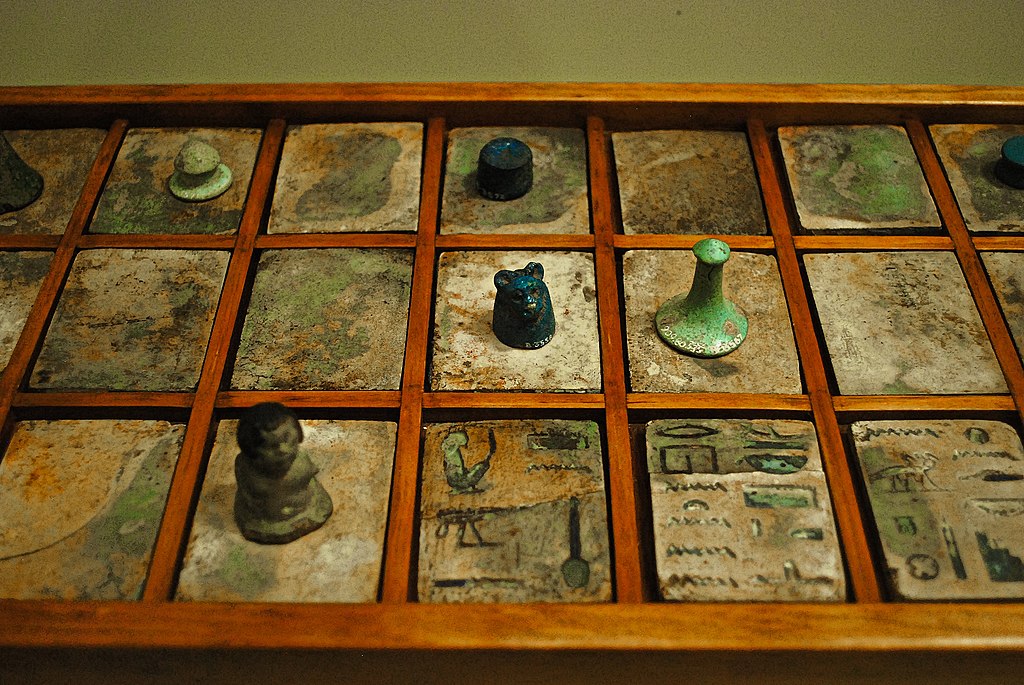 Photo by Enoch Leung on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Enoch Leung on Wikimedia Commons
10. Papyrus: The Ancient Paper
Egyptians developed papyrus, a form of early paper, from the papyrus plant. It was used for everything from writing to boat construction.
 Photo by Loren Biser on Unsplash
Photo by Loren Biser on Unsplash
11. Beer Consumption
Beer was a dietary staple in ancient Egypt. Workers were often paid in beer, and it was consumed daily by people of all social classes.
 Photo by Vassil on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Vassil on Wikimedia Commons
12. Cats: Revered and Protected
Cats were considered sacred in ancient Egypt. Killing one, even accidentally, could result in severe punishment.
 Photo by Matheus Queiroz on Unsplash
Photo by Matheus Queiroz on Unsplash
13. Hieroglyphics Decoded
The Rosetta Stone, discovered in 1799, had inscriptions in three scripts, enabling scholars to decipher ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics.
 Photo by Vania Teofilo on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Vania Teofilo on Wikimedia Commons
14. Nileometer: Measuring the Nile
Egyptians used a tool called the "Nileometer" to measure the river's water levels. This helped them predict and prepare for the annual floods.
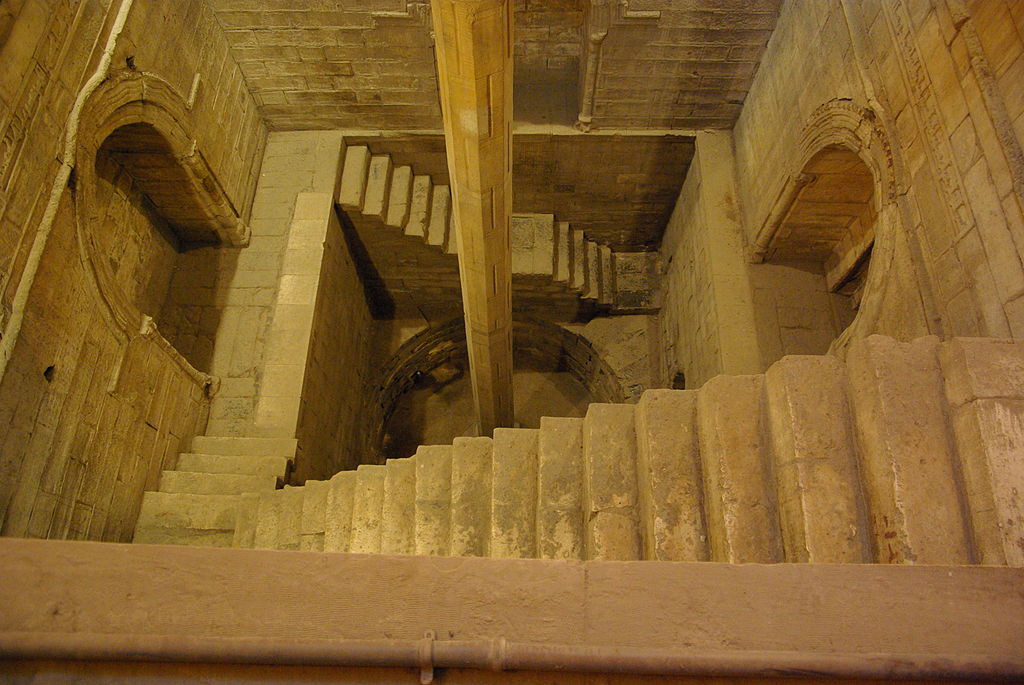 Photo by Berthold Werner on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Berthold Werner on Wikimedia Commons
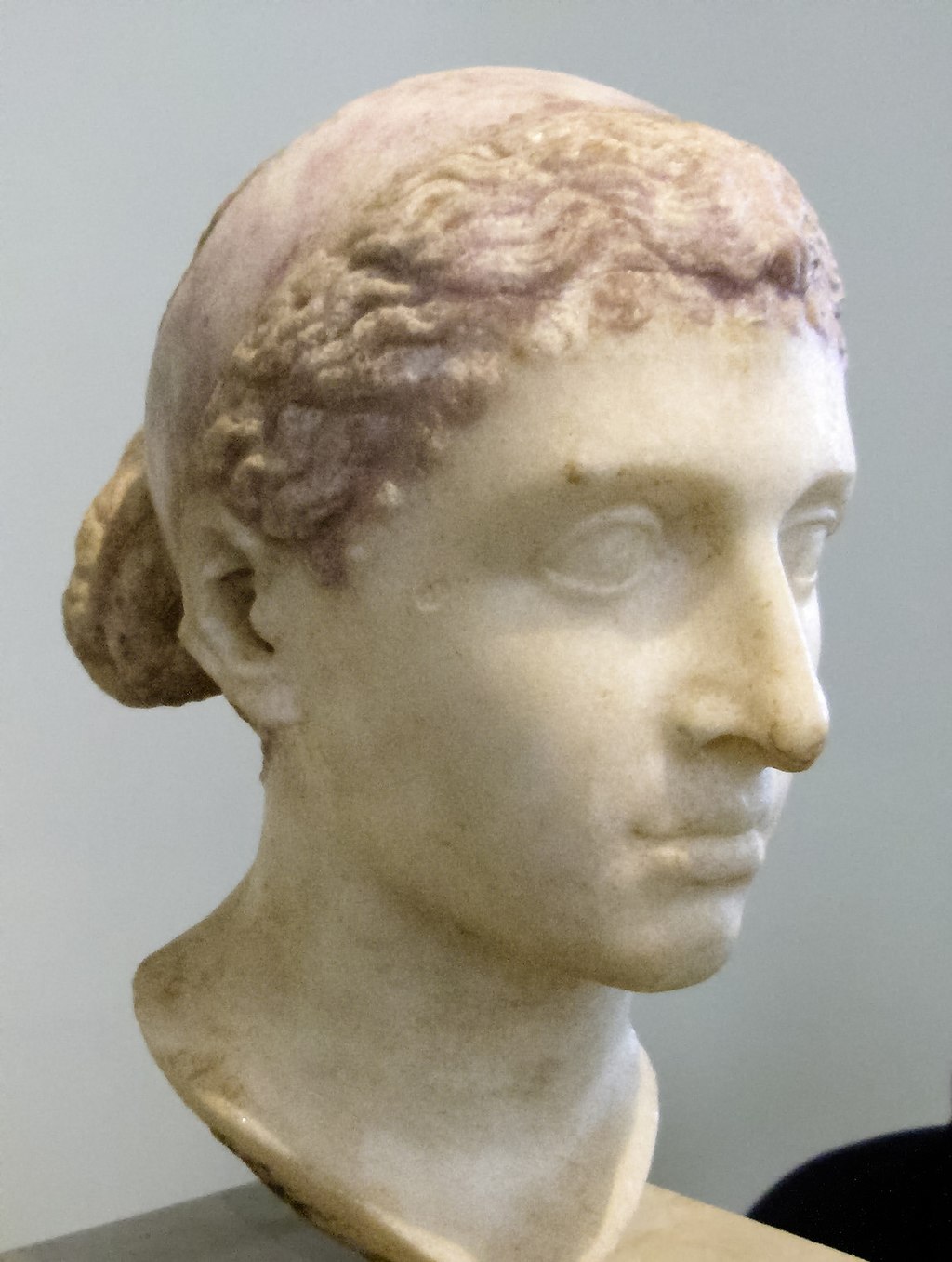
15. Cleopatra: The Greek Pharaoh
Although Cleopatra is famous as an Egyptian queen, she was of Greek descent and was the last Pharaoh of the Ptolemaic dynasty.
 Louis le Grand, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Louis le Grand, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
16. Medicine and Surgery Pioneers
Ancient Egyptians practiced advanced medicine and even had specialized doctors for various body parts. They performed surgeries, dental procedures, and had a vast array of medicinal recipes.
 Photo by Online Marketing on Unsplash
Photo by Online Marketing on Unsplash
17. Perfumes and Fragrances
Egyptians were pioneers in the production and use of perfumes. They used various oils, resins, and aromatic plants to create fragrances for ceremonies and daily life.
 Photo by Laura Chouette on Unsplash
Photo by Laura Chouette on Unsplash
18. Sun Worship: The Solar Disk
Amenhotep IV changed his name to Akhenaten and promoted the worship of the sun disk, Aten. This was one of the earliest forms of monotheism in history.
 Photo by Neoclassicism Enthusiast on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Neoclassicism Enthusiast on Wikimedia Commons
19. Dream Interpretation
Dreams held significant importance in ancient Egypt, and there were specific dream interpreters. Various papyri have been discovered that list common dreams and their meanings.
 Photo by Kinga Howard on Unsplash
Photo by Kinga Howard on Unsplash
20. Shipbuilding and Maritime Expeditions
The Egyptians were excellent shipbuilders and organized maritime expeditions to distant lands. The "Wadi al-Jarf" papyri describe the logistics of building ships and the daily life of workers at the Red Sea port.
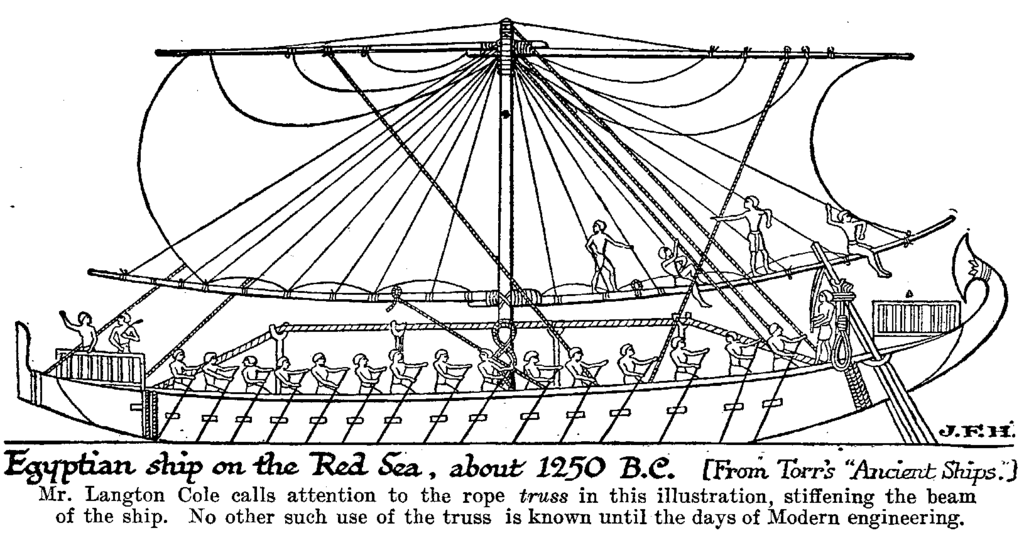 Photo by J. F. Horrabin (1884-1962), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Photo by J. F. Horrabin (1884-1962), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
21. World’s Oldest Dress
A dress found in Egypt, dating back to around 3482-3102 B.C., is considered the world’s oldest woven garment. It's very plain - a simple V-neck tunic with narrow sleeves.
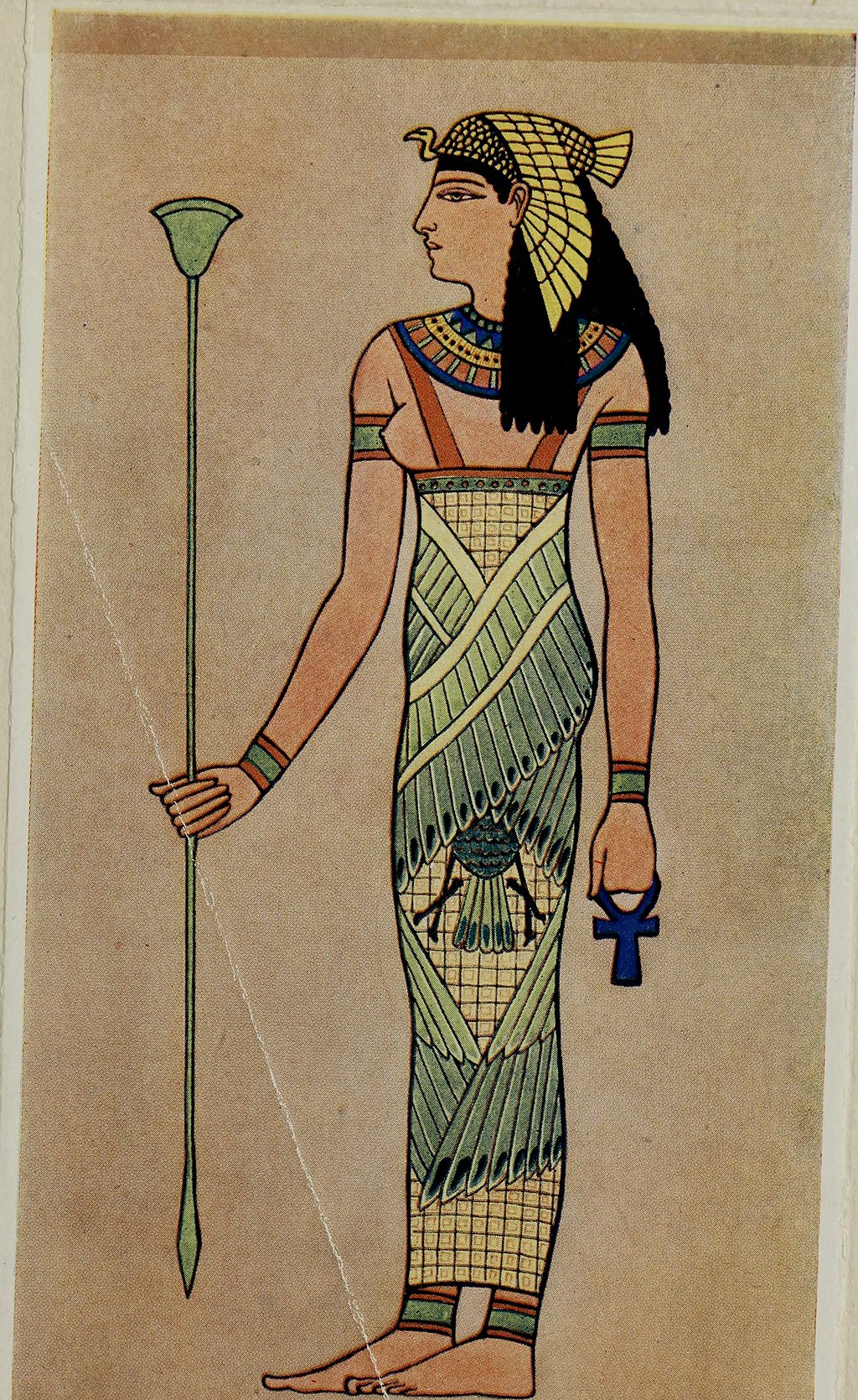 Photo by Houston, Mary G. (Mary Galway), b. 1871 on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Houston, Mary G. (Mary Galway), b. 1871 on Wikimedia Commons
22. Shaved Heads for Cleanliness
Ancient Egyptians often shaved their heads and wore wigs. This helped combat lice and maintain cleanliness in the hot climate.
 Photo by Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
23. First Labor Strike
The first recorded labor strike in history took place during Ramses III’s reign. Workers on the pyramids protested delayed payments in the form of food.
 Photo by Leonardo Ramos on Unsplash
Photo by Leonardo Ramos on Unsplash
24. Beauty Marks
Ancient Egyptian women placed a cone of scented fat on their heads. As it melted, it released fragrance, functioning like a perfume.
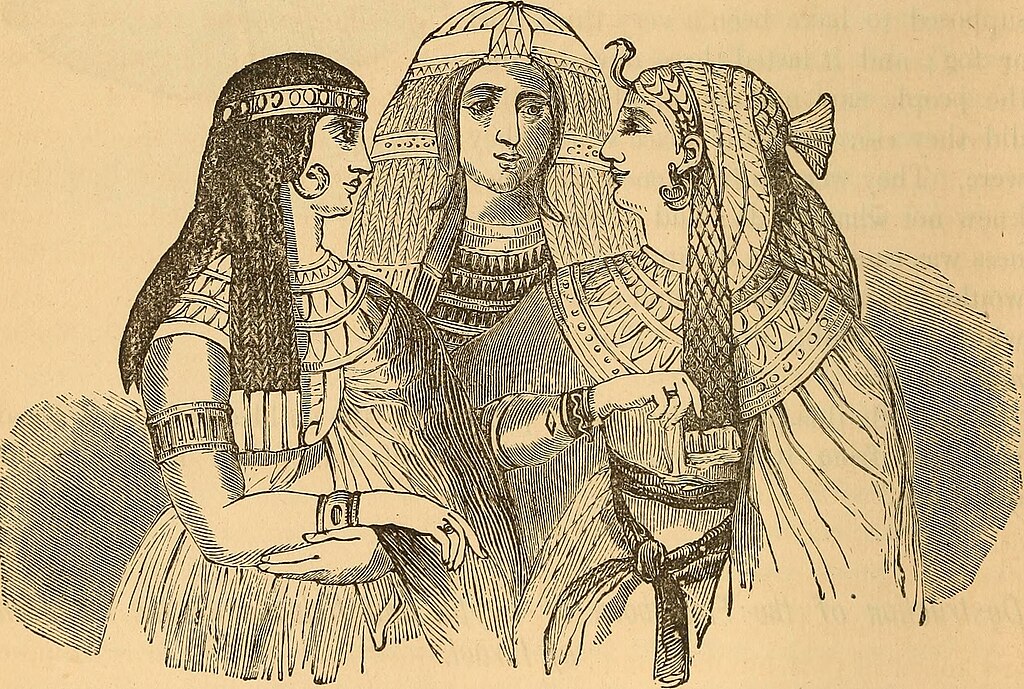 Internet Archive Book Images, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons
Internet Archive Book Images, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons
25. Advanced Medical Texts
The Edwin Smith Papyrus is an ancient Egyptian medical text detailing surgical knowledge. It’s the world’s oldest known surgical treatise.
 Photo by Jeff Dahl, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Jeff Dahl, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
26. Land of Gold
The Egyptians called their country “Kemet,” meaning “Black Land” due to the rich, dark soil. They also referred to it as “Nubt,” meaning “Gold,” due to their rich gold mines.
 Photo by Maksim Sokolov (maxergon.com) on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Maksim Sokolov (maxergon.com) on Wikimedia Commons
27. Unique Writing Direction
Hieroglyphic inscriptions could be written in any direction: left-to-right, right-to-left, or top-to-bottom. The reader would follow the direction that the symbols (like animal heads) were facing.
 Photo by AXP Photography on Unsplash
Photo by AXP Photography on Unsplash
28. Sandals with Messages
Some ancient Egyptian sandals were found with inscriptions on their soles. They might contain messages or symbols, so that they left imprints when worn.
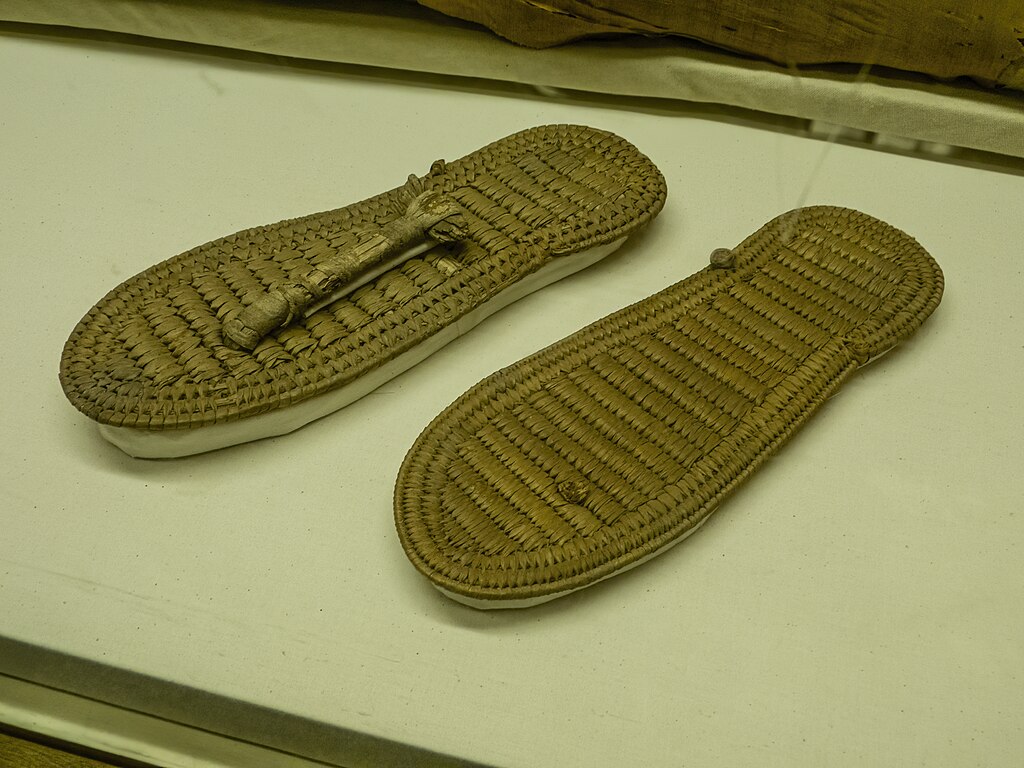 Photo by Mary Harrsch on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Mary Harrsch on Wikimedia Commons
29. A Festival of Drunkenness
Egyptians held a festival called "The Feast of Drunkenness" to honor Sekhmet, a lion-headed goddess. It involved music, sex, and, as the name implies, getting intoxicated.
 Photo by Jean-Pol GRANDMONT on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Jean-Pol GRANDMONT on Wikimedia Commons
30. Sphinx's Lost Nose
There's a myth that Napoleon's troops shot off the Sphinx's nose, but drawings from before Napoleon's time show the nose already missing. The true cause remains a mystery.
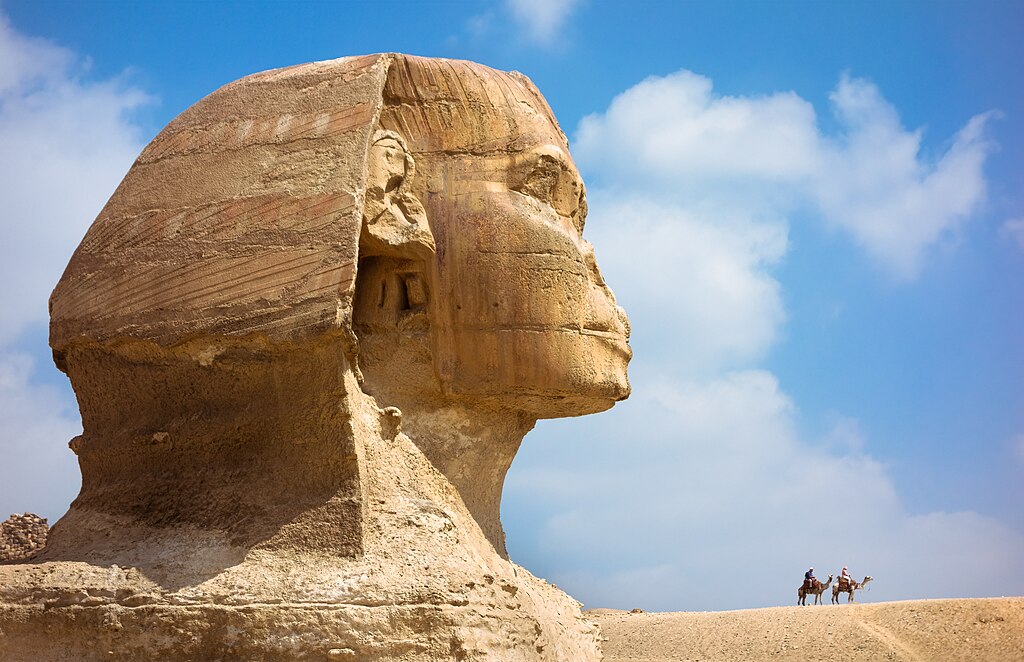 Photo by Petar Milošević on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Petar Milošević on Wikimedia Commons
31. Animal Mummies
Not only did Egyptians mummify humans, but also animals like cats, birds, and crocodiles. These were often given as offerings to gods.
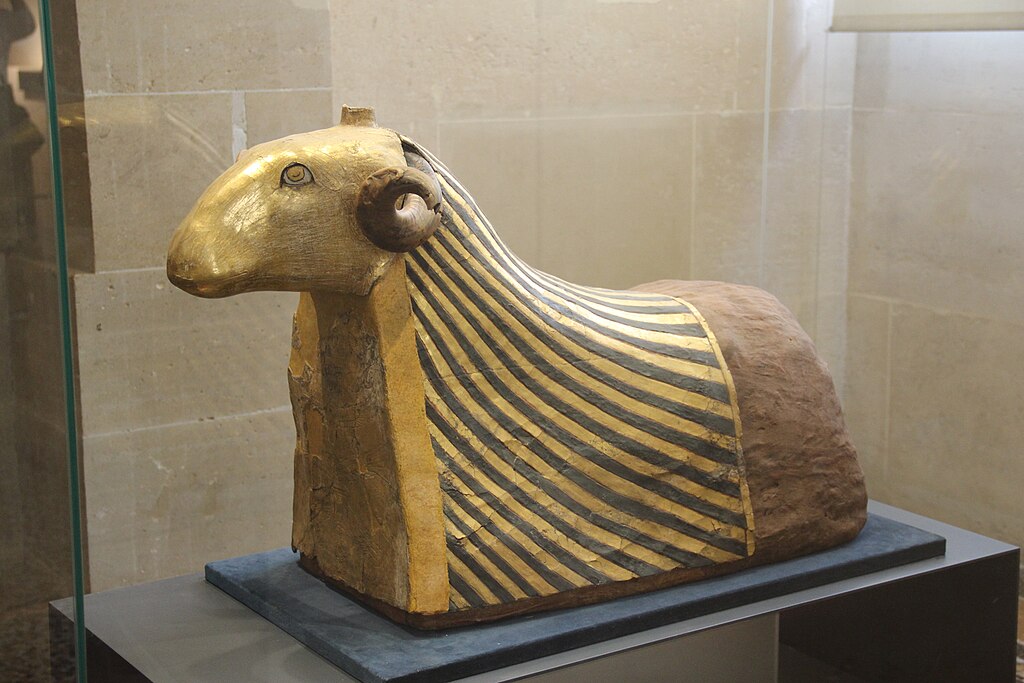 Photo by Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
32. The Diverse Pantheon
Ancient Egyptians had over 2,000 deities. They ranged from major gods worshipped nationwide to minor local deities.
 Internet Archive Book Images, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons
Internet Archive Book Images, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons
33. World's Oldest Prosthetic
An artificial toe found on a mummy is considered the world’s oldest functional prosthetic. It shows advanced craftsmanship, suggesting an understanding of human anatomy.
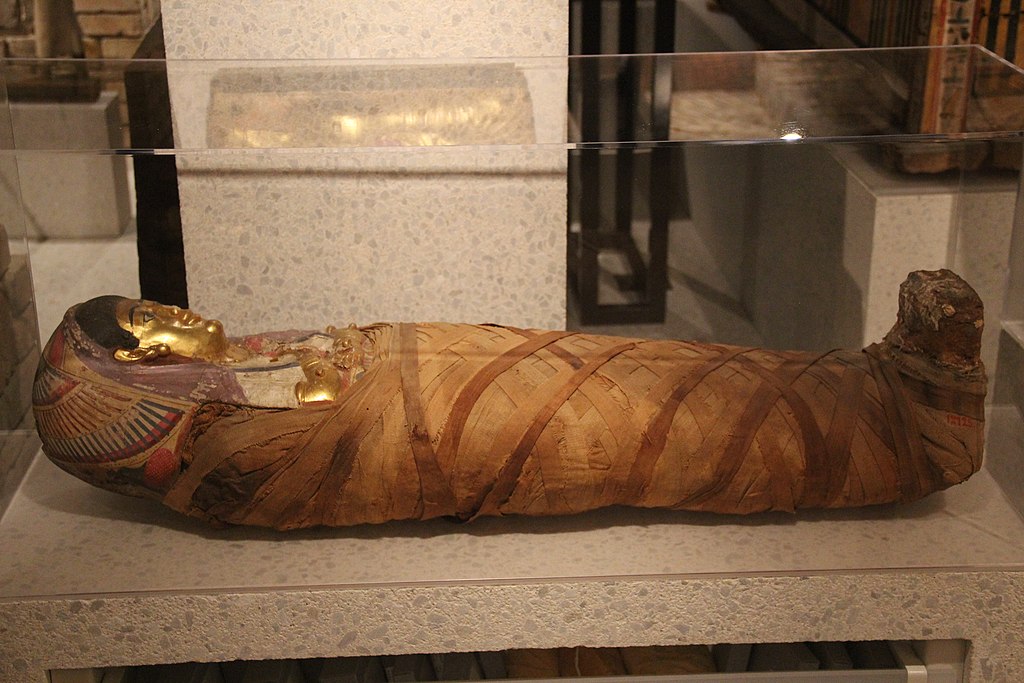 Photo by Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
34. Pyramid Construction Theories
While many theories exist about how pyramids were built, the exact techniques remain a subject of debate. Some believe they used straight ramps, while others think spiral ramps were employed.
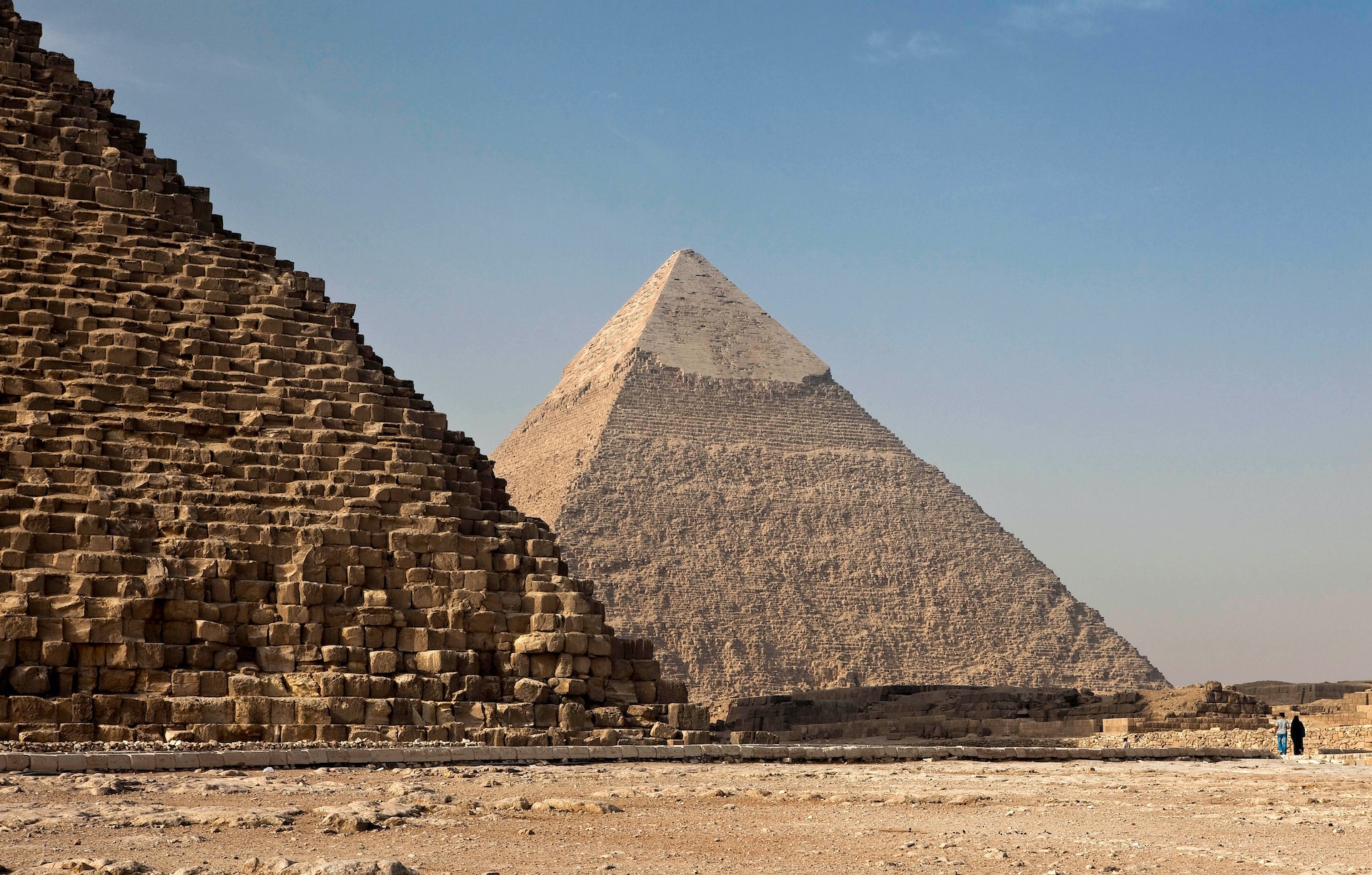 Photo by Ricardo Gomez Angel on Unsplash
Photo by Ricardo Gomez Angel on Unsplash
35. Eye of Horus: Symbol of Protection
The Eye of Horus was a prominent symbol, representing protection, royal power, and good health. Egyptians often wore amulets shaped like this eye.
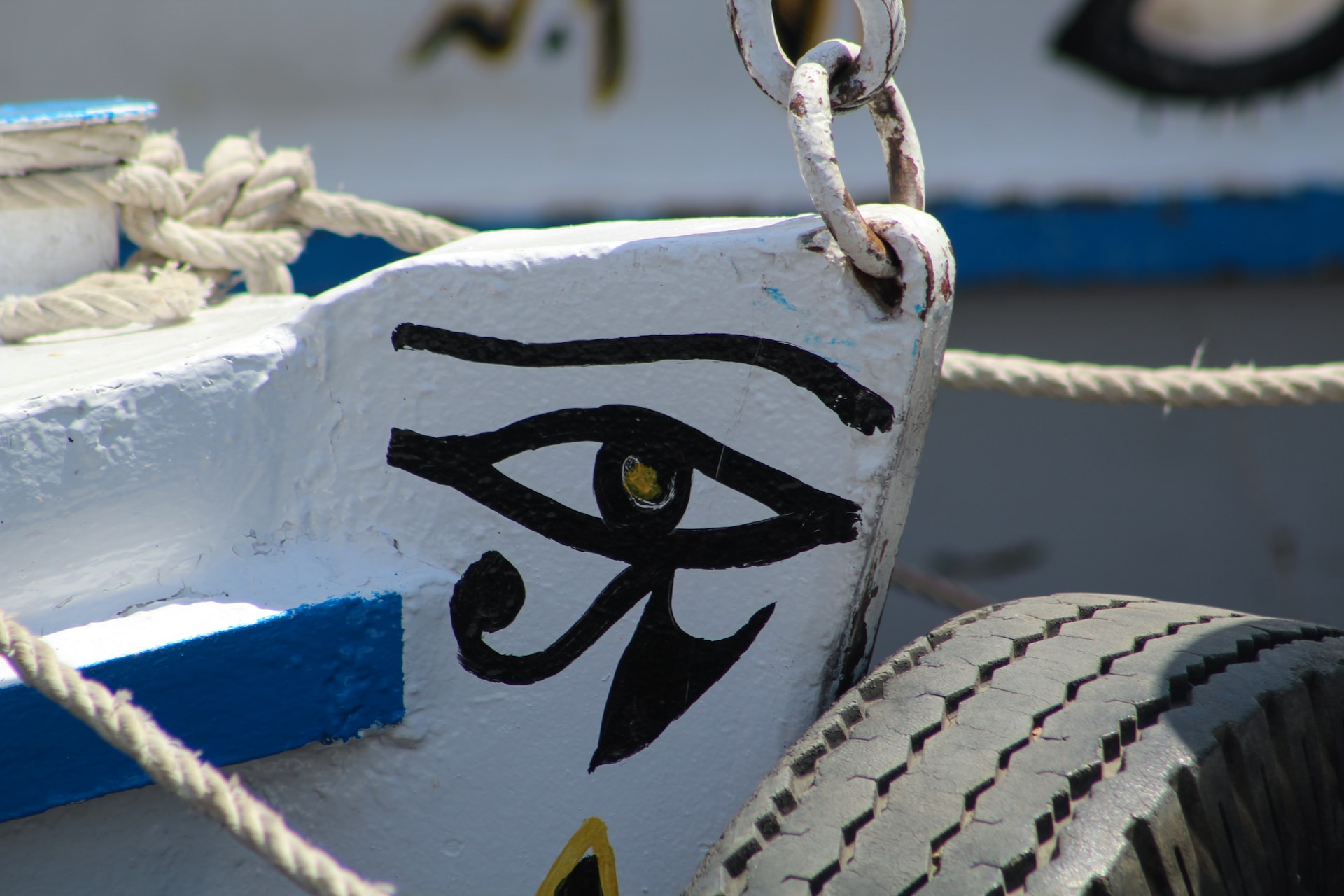 Photo by Carlota O. on Unsplash
Photo by Carlota O. on Unsplash
36. Royal Women’s Power
Hatshepsut, one of ancient Egypt’s female pharaohs, donned male attire to assert her authority. She ruled successfully for over two decades.
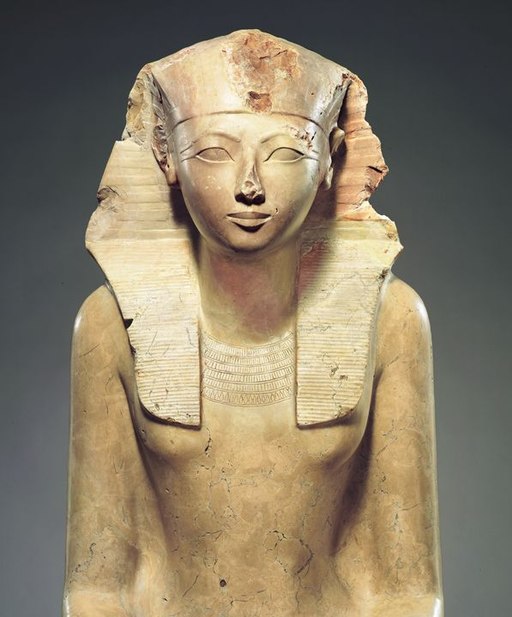 Photo by Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
37. Mysteries of the Saqqara Bird
A wooden artifact, called the Saqqara Bird, resembles a modern airplane. Some believe it demonstrates knowledge of aerodynamics, though it's often thought to represent a bird.
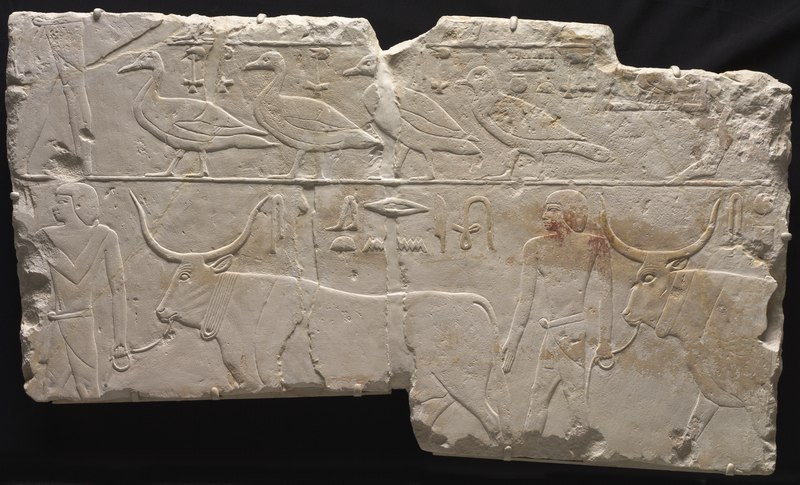 Photo by Cleveland Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Cleveland Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
38. Beauty Standards
Green eye makeup (made from malachite) and black kohl eyeliner were beauty essentials. They not only enhanced appearance but also offered protection from the sun’s glare.
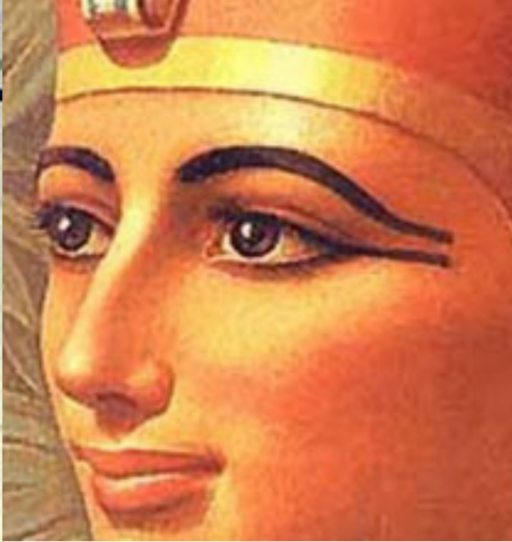 Photo by Crystal Gabriela on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Crystal Gabriela on Wikimedia Commons
39. The Role of Dwarfs
Dwarfs held special roles in Egyptian society, often revered and associated with gods like Bes. Many served in prominent capacities in households and temples.
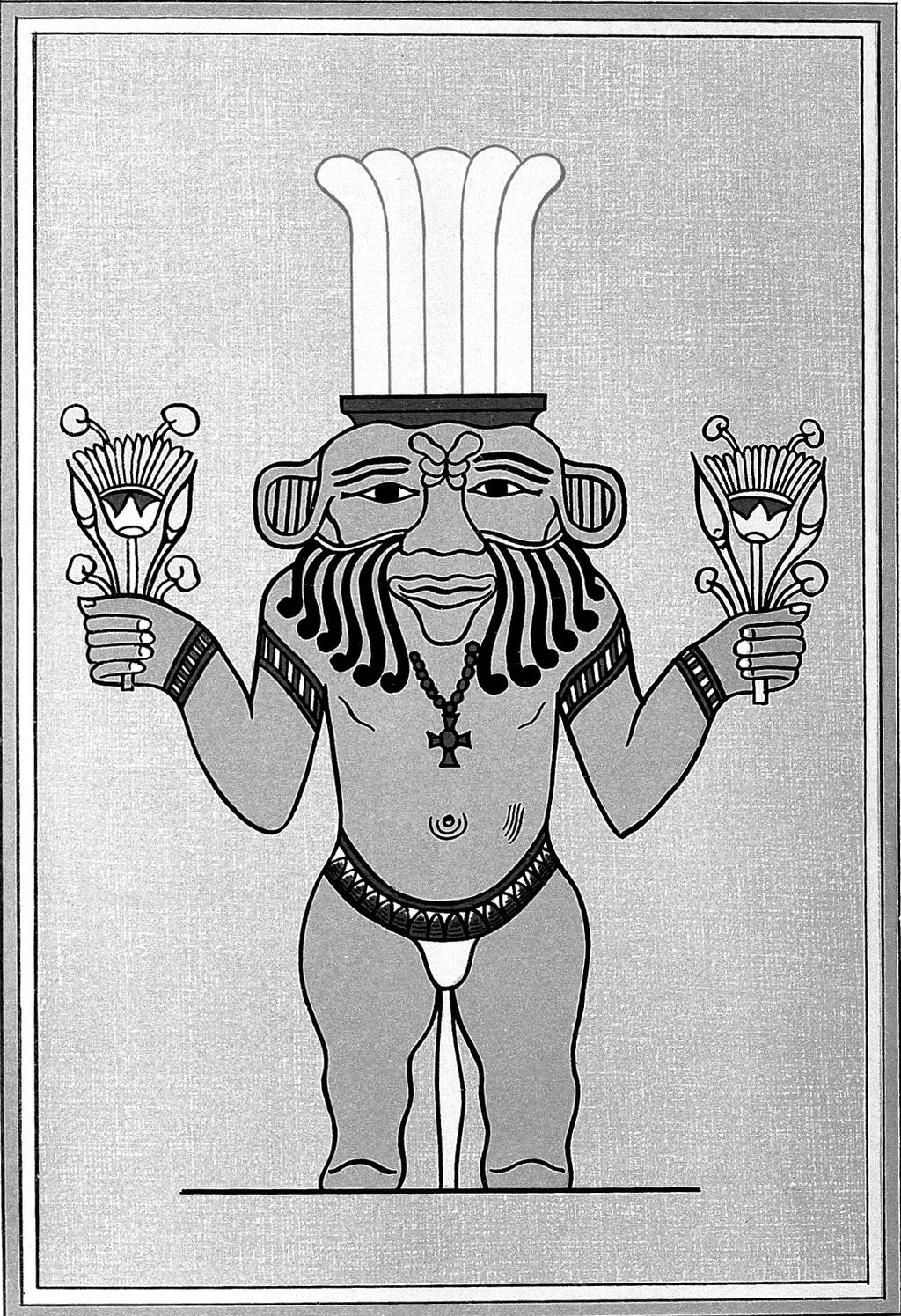 Photo by Unknown on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Unknown on Wikimedia Commons
40. The Lighthouse of Alexandria
One of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, the Lighthouse of Alexandria (Pharos of Alexandria), was an engineering marvel. Standing about 330 feet tall, it guided sailors safely into the harbor for centuries.
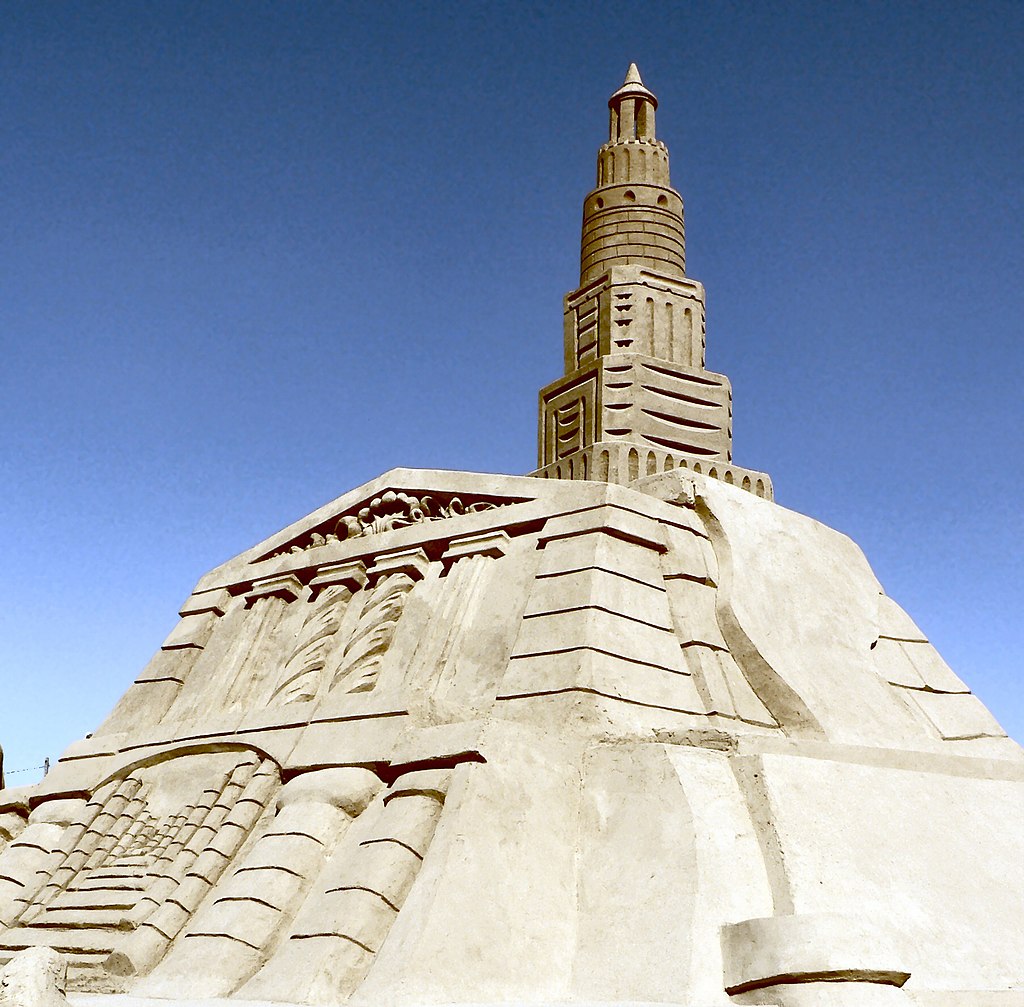 Photo by Paulo Juntas on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Paulo Juntas on Wikimedia Commons
41. Advanced Haircare
Egyptians took haircare seriously, with evidence of hair gel usage discovered on mummies. They used plant oils and fats to style and maintain their hairdos.
 Photo by Tim Mossholder on Unsplash
Photo by Tim Mossholder on Unsplash
42. The Worship of Dung Beetles
Scarab beetles, or dung beetles, were revered because they rolled balls of dung underground, symbolizing the sun’s journey. They became symbols of rebirth, with scarab amulets regularly used for protection.
 Photo by Chrumps on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Chrumps on Wikimedia Commons
43. A Unique Form of Pillows
Instead of soft pillows, ancient Egyptians used headrests made of wood or stone. These elevated the head, promoting air circulation and protecting elaborate hairstyles from getting ruined.
 Photo by Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
44. Timekeeping Devices
Egyptians used sundials to tell the time during the day and water clocks for nighttime. The water clock consisted of a pot with a small hole, letting water drip at a steady rate, marking the passing hours.
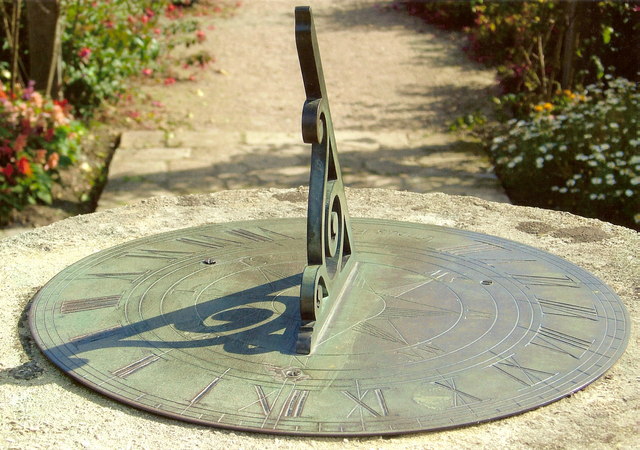 Photo by adam sommerville on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by adam sommerville on Wikimedia Commons
45. Breath Mints for Oral Hygiene
Given the diet and dental issues, bad breath was a concern. To combat this, Egyptians chewed on herbs and created early forms of breath mints using ingredients like frankincense and myrrh.
 Photo by Themightyquill on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Themightyquill on Wikimedia Commons
46. A Society Built on Beer and Bread
Beer and bread, often made in the same facilities, were staples of the Egyptian diet. The beer was a thick, porridge-like substance, and sometimes herbs were added for flavoring.
 Jon Sullivan, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Jon Sullivan, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
47. First Known Peacekeeping
Force The "Medjay" was an ancient Egyptian paramilitary force, originally a desert tribe, that later became an elite military unit. They protected valuable areas, especially royal and sacred sites, from thieves.
 Joseph Bonomi, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Joseph Bonomi, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
48. A Game of 20
Squares "Aseb" was another popular board game, distinct from Senet. Players used a set of knucklebone dice to advance their pieces on a board of 20 squares.
 Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
49. Tattooing in Ancient Egypt
Tattoos have been discovered on mummies, especially on female ones, often around the lower abdomen, thighs, and chest. It’s believed these tattoos had a therapeutic or protective function.
 Photo by Noctuark on Wikimedia Commons
Photo by Noctuark on Wikimedia Commons
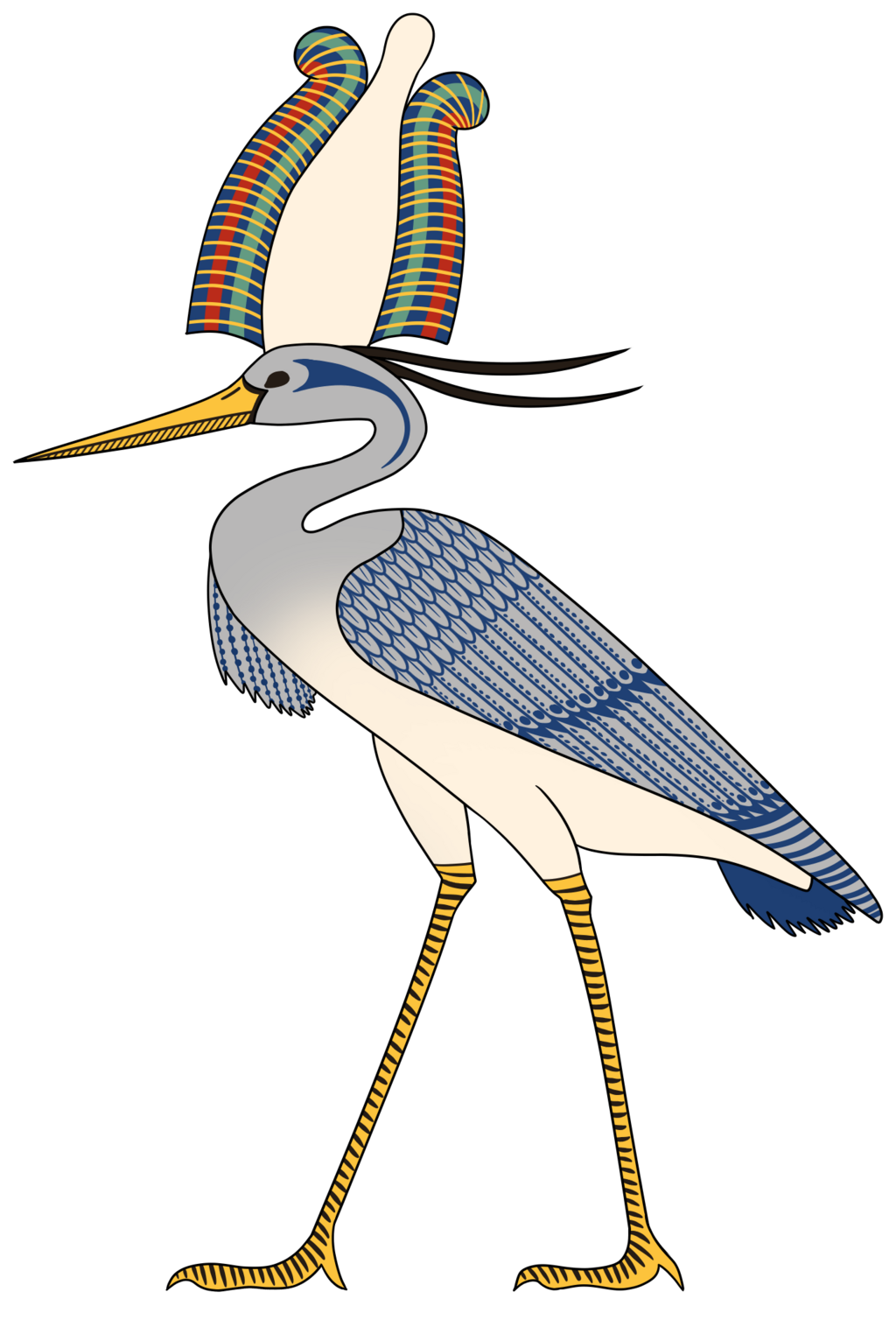
50. The Sacred Bennu Bird
The Bennu bird, resembling a heron, was linked to the sun and rebirth. Some believe the Bennu was the inspiration for the legendary Phoenix in later cultures.








